Cloud computing has become an indispensable part of the modern business landscape. Businesses of all sizes rely on cloud providers for a multitude of services, from basic data storage and website hosting to complex applications and machine learning capabilities. A crucial aspect of selecting a cloud provider is understanding their Service Level Agreement (SLA). A cloud SLA outlines the provider’s commitment to service performance, availability, and support, setting clear expectations for both the provider and the client. Thoroughly understanding cloud SLAs is paramount for ensuring your business operations run smoothly and efficiently.
This article will delve into the intricacies of cloud SLAs, equipping you with the knowledge necessary to evaluate and compare offerings from different cloud providers. We’ll explore key performance indicators (KPIs) outlined in SLAs, including uptime, latency, and data durability, and discuss their significance for your business. We’ll also examine what happens when a cloud provider fails to meet their SLA obligations, and what recourse you might have. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of cloud SLAs and be better prepared to choose a provider that meets your specific business needs.
What Is a Cloud SLA?
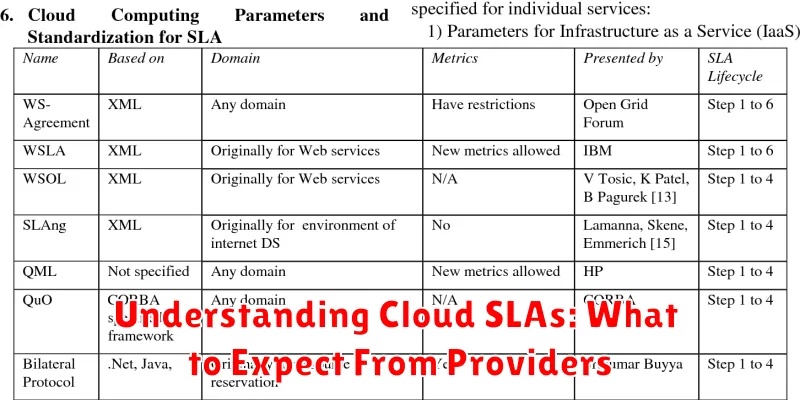
A Cloud Service Level Agreement (SLA) is a formal contract between a cloud provider and a customer that outlines the expected performance and availability of the cloud service. It acts as a guarantee of the minimum level of service that the provider will deliver.
The SLA details specific metrics, like uptime, latency, and data durability. It also defines the responsibilities of both the provider and the customer, including support procedures and issue resolution processes.
SLAs are critical for businesses relying on cloud services. They provide a framework for managing expectations, ensuring accountability, and offering a recourse mechanism if the provider fails to meet the agreed-upon service levels. Penalties for not meeting the SLA, such as service credits or refunds, are typically outlined within the agreement.
By clearly defining performance standards and consequences for not meeting them, cloud SLAs help establish a foundation of trust and transparency between the provider and the customer.
Key Components of a Typical SLA
A Service Level Agreement (SLA) outlines the expected performance and availability of a service. Uptime is a crucial component, often expressed as a percentage (e.g., 99.9%). This metric guarantees the service’s operational status for a specified period.
Performance metrics define acceptable response times and latency. These measurements ensure the service operates efficiently and meets user expectations. SLAs also define support procedures, outlining how and when customers can access technical assistance. This includes response times for different severity levels.
Compensation clauses detail remedies for breaches in the agreed-upon service levels. This often involves financial credits or other forms of restitution. Finally, security measures may be included, outlining the provider’s commitment to data protection and security protocols.
Uptime Guarantees and Penalty Clauses
A crucial aspect of any Cloud Service Level Agreement (SLA) is the uptime guarantee. This specifies the percentage of time the service provider guarantees their services will be operational and accessible. Common uptime guarantees range from 99.9% to 99.999%, with each “nine” representing a significant reduction in potential downtime. For example, 99.9% uptime allows for approximately 8.76 hours of downtime per year, while 99.999% allows for only about 5.26 minutes.
Closely related to the uptime guarantee are penalty clauses. These outline the repercussions for the provider if they fail to meet the agreed-upon uptime. Penalties typically involve service credits or financial compensation, often calculated as a percentage of the monthly fee for each percentage point of uptime missed. It’s essential to carefully review these clauses, noting how downtime is calculated and what constitutes eligible downtime. Planned maintenance, for instance, is often excluded from downtime calculations.
How to Evaluate a Provider’s SLA
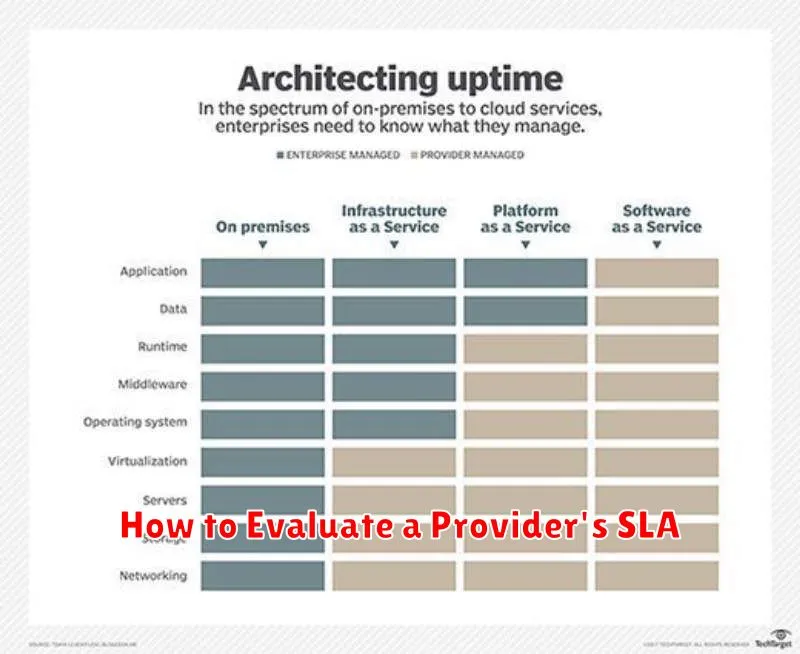
Evaluating a Service Level Agreement (SLA) requires careful consideration of several key components. Begin by examining the uptime guarantee. This percentage represents the promised availability of the service. A higher percentage is generally better, with many providers targeting 99.9% or higher. However, understand how this is calculated and what constitutes downtime.
Next, look at the performance metrics outlined in the SLA. These might include latency, throughput, and error rates. Ensure these metrics align with your application’s requirements. Consider whether the SLA provides clearly defined remediation procedures in case of service disruptions. Knowing how the provider will address and resolve issues is crucial.
Penalties or service credits offered for SLA breaches are another important factor. These compensate you for downtime or performance issues. Evaluate the structure of these credits and ensure they adequately reflect the impact of potential service disruptions on your business. Finally, carefully review the exclusions and limitations defined within the SLA. These define circumstances where the provider is not held responsible for downtime or performance issues, such as scheduled maintenance or events outside their control.
SLA vs SLO vs SLI: What’s the Difference?
These three terms are crucial for understanding cloud service reliability. While related, they represent distinct aspects of service performance. SLI (Service Level Indicator) measures a specific aspect of a service’s performance. Think of it as the raw data. Examples include uptime percentage, error rate, or latency.
An SLO (Service Level Objective) defines the target value or range for an SLI. It’s the performance goal the provider aims to achieve. For example, an SLO might be 99.9% uptime. SLOs are typically more understandable and business-focused than SLIs.
Finally, the SLA (Service Level Agreement) is a formal contract between the provider and customer. It outlines the SLOs, consequences of not meeting those SLOs (e.g., financial penalties), and other service-related commitments. The SLA holds the provider accountable for meeting their performance promises. It’s the legally binding document that solidifies the expectations around service performance.
Common Pitfalls to Watch Out For
While cloud SLAs offer valuable assurances, it’s crucial to be aware of potential pitfalls. One common oversight is focusing solely on the uptime percentage. A 99.99% uptime still allows for nearly an hour of downtime per year. Consider how this downtime could impact your specific business operations.
Another pitfall is neglecting to thoroughly understand the definition of downtime within the SLA. Different providers may have varying interpretations. Some may only consider complete outages, while others may include performance degradation below a certain threshold.
Exclusions within the SLA also warrant careful attention. Scheduled maintenance, force majeure events, and issues stemming from customer actions are often excluded from uptime guarantees. Be aware of these exclusions to avoid unrealistic expectations.
Finally, remember that SLAs are legally binding agreements. Ensure you fully comprehend the terms and conditions before committing to a provider. Failing to do so could leave you with limited recourse in the event of an outage.
Negotiating a Better SLA for Your Business

While standard SLAs provide a baseline of service expectations, negotiating a better SLA tailored to your specific business needs can be highly beneficial. Clearly define your critical requirements. Identify which aspects of the service are most crucial for your operations, such as uptime, latency, or support response times. Quantify these requirements with specific metrics.
Understand the provider’s limitations and flexibility. Not all providers are willing to negotiate every aspect of their SLA. Larger providers may have more standardized offerings, while smaller providers might be more open to customization. Research their past performance and customer reviews to gauge their reliability.
Focus on key metrics. Don’t attempt to negotiate every single clause. Prioritize the metrics that directly impact your business’s performance and revenue. For example, if your business relies heavily on real-time data processing, prioritize low latency over other metrics.
Consider tiered SLAs. Different applications or services within your business may have different requirements. Negotiate tiered SLAs that offer varying levels of service for different components of your infrastructure. This allows you to optimize costs while ensuring critical services receive the highest level of support.
Document everything. Ensure all agreed-upon modifications and additions to the standard SLA are clearly documented and signed by both parties. This prevents misunderstandings and provides a clear framework for resolving potential disputes.