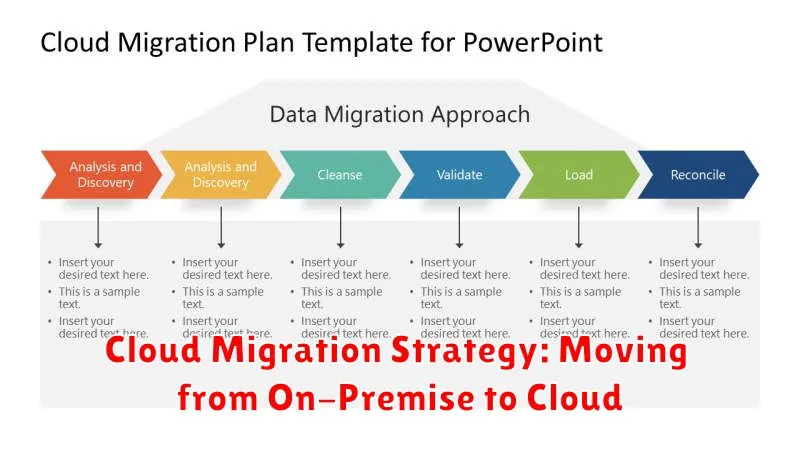
Embarking on a cloud migration journey can be a transformative step for any organization. Migrating from a traditional on-premise infrastructure to the cloud offers compelling advantages, including enhanced scalability, improved cost-efficiency, and increased agility. Developing a comprehensive cloud migration strategy is crucial for success, ensuring a smooth transition and maximizing the benefits of the cloud environment. This involves careful planning, assessment, and execution, addressing key considerations such as application compatibility, security requirements, and data migration complexities. Understanding the various cloud service models (IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS) is essential in selecting the right platform for your specific needs. A well-defined cloud migration strategy will pave the way for a successful transition to the cloud, enabling your organization to harness the full potential of modern cloud computing.
This article will delve into the essential components of a successful cloud migration strategy. We will explore the critical steps involved in migrating from on-premise to the cloud, outlining best practices and addressing common challenges. From initial assessment and planning to execution and post-migration optimization, we will provide a comprehensive guide for organizations looking to leverage the cloud‘s transformative power. We will discuss key considerations such as choosing the right cloud provider (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, etc.), selecting the appropriate cloud deployment model (public, private, or hybrid), and managing security and compliance in the cloud. By following a well-defined cloud migration strategy, organizations can minimize risks, reduce costs, and unlock the full potential of the cloud.
Why Migrate to the Cloud?
Migrating to the cloud offers compelling advantages for businesses of all sizes. Cost savings are a primary driver, eliminating the need for substantial upfront investments in hardware and reducing ongoing maintenance expenses. Cloud providers handle infrastructure management, freeing up internal IT resources to focus on strategic initiatives.
Scalability and flexibility are key benefits. Cloud resources can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing business demands, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency. This agility allows organizations to adapt quickly to market fluctuations and seize new opportunities.
Enhanced security is another compelling reason. Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, often exceeding the capabilities of individual organizations. Data backups, disaster recovery, and business continuity are simplified and strengthened in the cloud environment.
Increased collaboration and accessibility are also significant advantages. Cloud-based applications and data can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, fostering teamwork and productivity. This enables remote work capabilities and supports a more flexible and distributed workforce.
Assessing Your Current Infrastructure
A crucial first step in any cloud migration strategy is a thorough assessment of your existing on-premise infrastructure. This assessment provides a clear understanding of your current IT landscape, enabling informed decisions about what to migrate, when, and how.
Begin by documenting all hardware components, including servers, storage devices, and network equipment. Specify their age, capacity, and current utilization rates. This inventory serves as a baseline for determining future cloud resource requirements.
Next, analyze your software applications. Identify dependencies, performance requirements, and potential compatibility issues with your chosen cloud environment. Categorize applications based on their suitability for cloud migration, considering factors like complexity and business criticality.
Evaluate your current IT spending, including hardware maintenance, software licenses, and staffing costs. This financial analysis will help you understand the potential cost savings and return on investment (ROI) of migrating to the cloud.
Finally, consider your organization’s security posture. Identify existing security measures and any regulatory compliance requirements that must be maintained during and after the migration.
Types of Migration: Lift-and-Shift, Refactor, Rebuild
Choosing the right cloud migration strategy is crucial for a successful transition. There are several approaches, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. Three common types are lift-and-shift, refactor, and rebuild.
Lift-and-shift, also known as rehosting, involves migrating applications to the cloud without significant modifications. This approach is the fastest and often the least expensive option. However, it may not fully leverage cloud-native features and could result in higher long-term costs.
Refactoring, or rearchitecting, involves modifying applications to better suit the cloud environment. This approach requires more effort than lift-and-shift but can lead to improved performance, scalability, and cost optimization by leveraging cloud-native services.
Rebuilding, or repurchasing, involves completely rebuilding applications from scratch in the cloud. This is the most complex and time-consuming option, but it allows for full optimization and the use of the latest cloud technologies. It’s often the best choice for legacy applications that are difficult or expensive to maintain.
Creating a Migration Roadmap
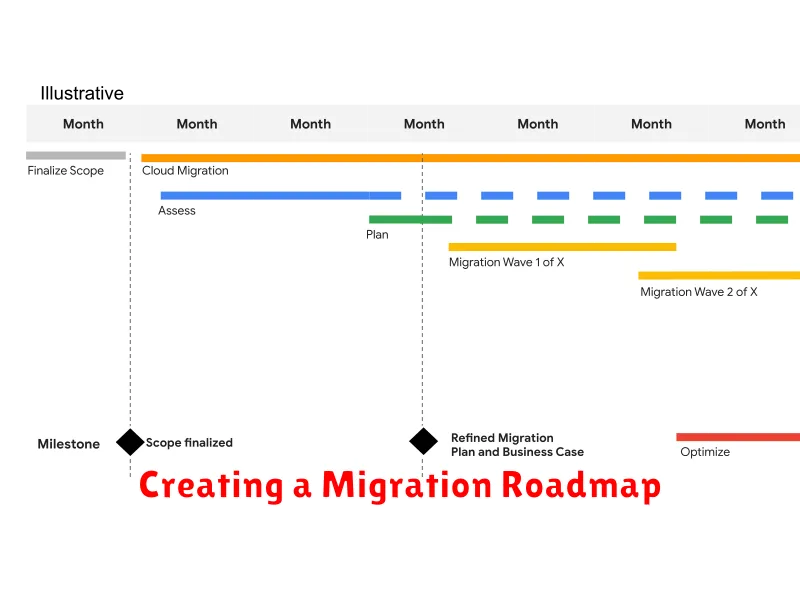
A well-defined roadmap is crucial for a successful cloud migration. It provides a structured plan, outlining the steps, timelines, and resources required for a smooth transition. This roadmap acts as a guide throughout the migration process, ensuring all stakeholders are aligned and working towards a common goal.
Begin by assessing your current on-premise infrastructure. Identify applications, dependencies, and data storage requirements. This assessment helps determine the optimal migration strategy, whether it’s rehosting, replatforming, refactoring, or repurchasing.
Next, prioritize applications for migration. Consider factors like business criticality, complexity, and interdependencies. A phased approach, migrating less critical applications first, allows for iterative learning and refinement of the process.
Establish a clear timeline for each phase of the migration. Include milestones, deadlines, and key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress. This ensures the migration stays on schedule and within budget.
Allocate resources effectively. Identify the team members responsible for each task and ensure they have the necessary skills and training. Resource allocation should consider both technical expertise and project management capabilities.
Tools That Simplify the Move
Migrating to the cloud can seem daunting, but various tools simplify the process. These tools automate and streamline different stages of the migration, reducing manual effort and potential errors. Choosing the right tools depends on factors like the source infrastructure, target cloud environment, and application complexity.
Assessment tools provide insights into your current IT landscape, identifying dependencies and potential migration challenges. They analyze on-premise resources, helping determine the optimal cloud configuration and estimate costs.
Migration tools facilitate the actual transfer of data and applications. These tools vary in capabilities, from lift-and-shift migrations to more complex refactoring scenarios. Some offer features like automated data replication and server provisioning.
Management tools offer ongoing support post-migration. These tools monitor cloud resources, manage costs, and ensure security and compliance within the new environment.
Testing and Validation Post-Migration
After migrating your systems to the cloud, thorough testing and validation are critical. This process ensures that all applications and services function as expected in the new cloud environment and meet the defined performance criteria. Testing methodologies should cover various aspects, including functionality, performance, security, and disaster recovery.
Functional testing confirms that all applications operate correctly in the cloud, replicating on-premise functionality. Performance testing assesses system responsiveness and stability under expected load conditions. Security testing validates the effectiveness of security controls and compliance with relevant regulations. Disaster recovery testing verifies the ability to restore services in the event of an outage.
Validation involves comparing pre-migration performance baselines with post-migration performance. This helps identify any discrepancies and areas for optimization. It is also important to validate data integrity to ensure no data loss or corruption occurred during the migration process.
Avoiding Common Migration Mistakes
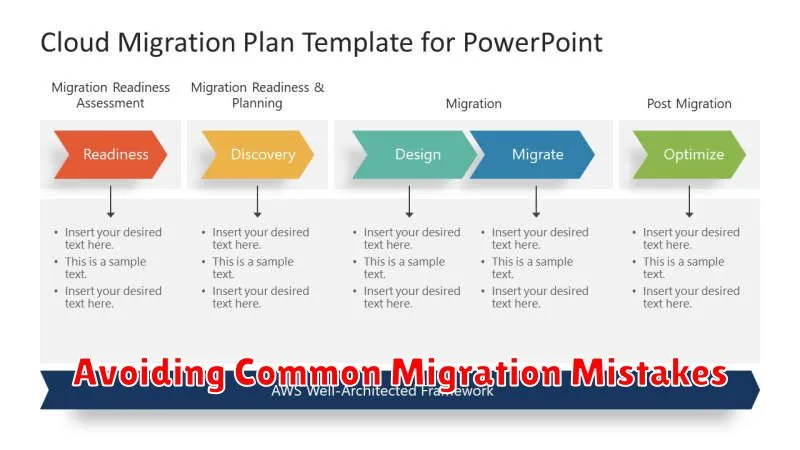
Migrating to the cloud offers significant advantages, but common pitfalls can hinder success. Lack of planning is a primary concern. A comprehensive strategy addressing security, compliance, and resource allocation is crucial.
Underestimating costs is another frequent error. Cloud pricing models can be complex. Failing to accurately predict ongoing operational expenses and data transfer costs can lead to unexpected budget overruns.
Ignoring application dependencies can create integration challenges. Thoroughly analyze application architecture and dependencies before initiating migration to ensure compatibility and smooth transitions.
Neglecting security considerations can expose vulnerabilities. Cloud security requires a different approach than on-premise. Implement robust security measures, including access controls, encryption, and regular security audits.
Inadequate testing can result in post-migration disruptions. Rigorous testing throughout the migration process is essential to validate functionality and performance.